Mexico’s Natural Gas Dilemma
FROM: OilPrice / Jude Clemente / 12 de febrero
Mexico’s 2013 energy reforms are based on bringing in more competition for the two state-owned monopolies that had become too stagnant, Pemex (oil and gas) and CFE (electricity). One of the key areas with huge upside for foreign firms is the very expensive process of natural gas storage, which is critical for Mexico as it moves to replace overused fuel oil and reduce GHG emissions to meet climate change goals.
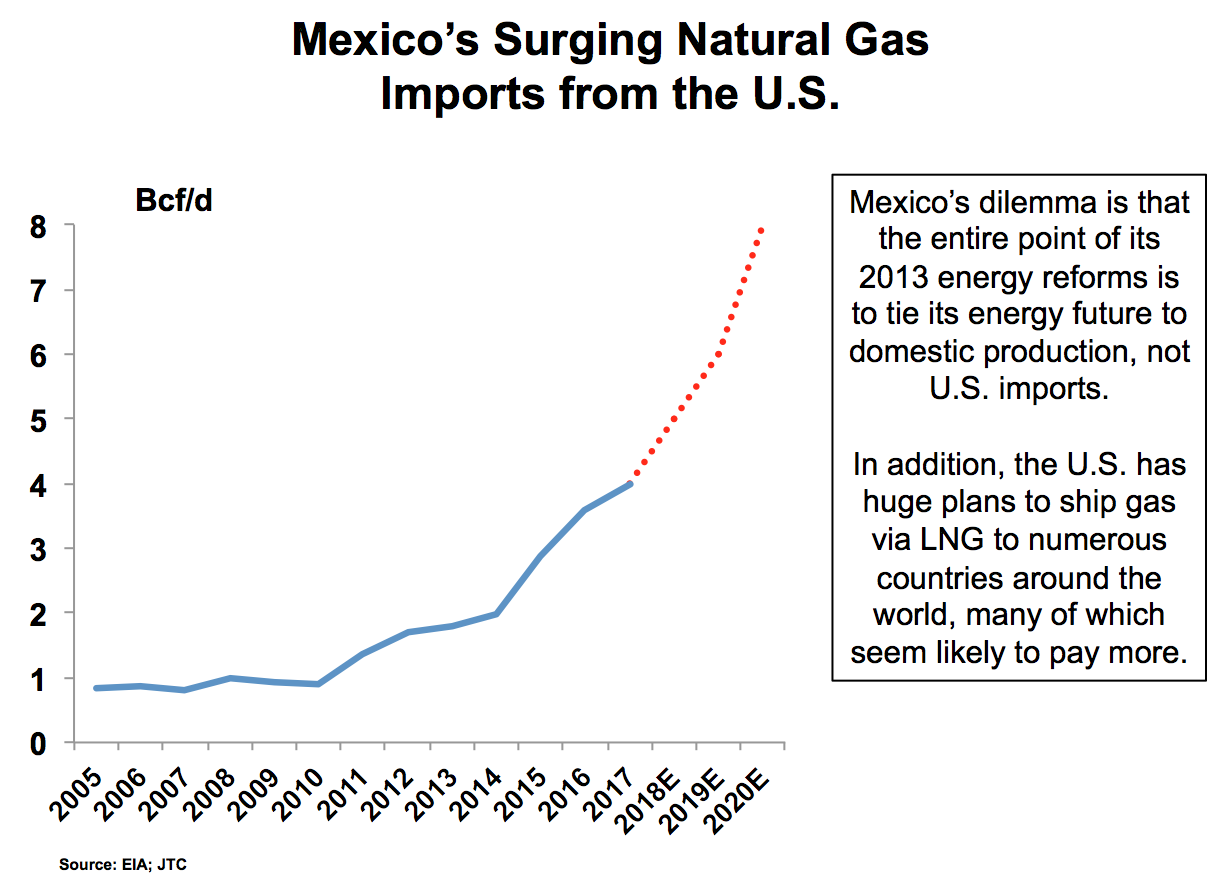
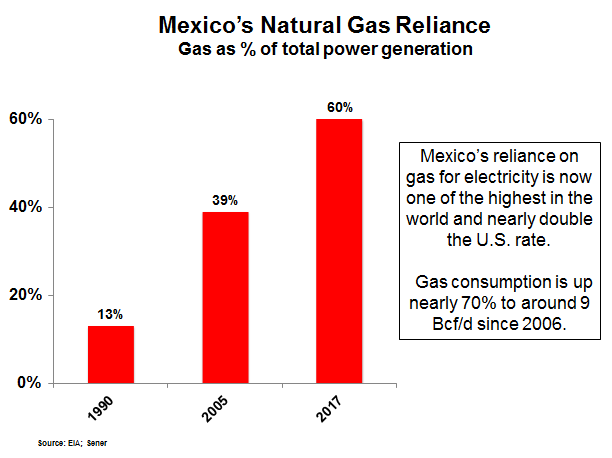
Despite rapidly declining production, Mexico is one of the most natural gas dependent nations on Earth. Gas now supplies 45 percent of all energy and 60 percent of electricity. Mexico has been forced to increasingly depend on cheaper piped imports from the U.S., which at 4.5 Bcf/d now account for about 55 percent of Mexico’s total gas usage. Much more gas will be required. Per capita, Mexico’s 130 million citizens consume just a third of the electricity that other OECD nations do. Additionally, there is a manufacturing boom in Mexico, namely in the automotive industry that will use increasing amounts of natural gas.
Currently with no underground sites, gas storage in Mexico will help even the market out — especially during high-demand times — and smooth bottlenecks that needlessly increase prices. Mexico now utilizes three LNG import terminals for short-term balancing, but this pricier supply is a problem for a nation where 50 percent of the people live below the poverty line. Mexico has been the largest buyer of U.S. LNG due to its dearth of pipelines. As seen during Hurricane Harvey, where officials had to force industrials to curtail operations, Mexico remains vulnerable to supply disruptions north of the border.
Today, the promotion of strategic gas inventories by the Mexican government should eventually lead to a commercial storage business with long-term, large-scale options. To start, the Energy Ministry (Sener) has been crafting a draft on storage policy, with the key proposal being a strategic reserve mandate for Sistrangas, the state-owned operator of Mexico’s largest pipeline network. The main policy requires the National Gas Control Center (Cenagas) to hold 45 Bcf of working gas in storage, which is still just what the country consumes in five days. So obviously, much more needs to be done in Mexico. Other OECD nations hold an average of at least 80 days’ worth of gas in storage.
For a sufficient storage market to emerge, Mexico needs to first better understand the seasonality of its own gas demand. Consumption in the U.S., for instance, can double in winter from summer because of heating needs, and the gas storage market has two phases: a “withdrawal season” from November–March and an “injection season” from April–October. Although not as dramatic, Mexico’s gas demand does peak in summer when hot temperatures surge electricity demand for air conditioners. To illustrate, U.S. gas exports to Mexico have typically been 35–50 percent higher in summer than winter.
Following the U.S. model, gas storage in Mexico also hinges on the private sector developing price indexes at pipeline interconnections and allowing regional price differences to materialize. Long reliant on U.S. gas based on price points at Henry Hub and Houston Ship Channel, Mexico seeks its own hub pricing system. This should occur sometime this year, likely first starting in the manufacturing hub of Monterrey, the capital city of the northeastern state Nuevo León. Going forward, rising trading volumes should help grow the immature market as well. Ultimately, commercial gas storage could become a viable business in Mexico within three to five years at the earliest.
Mexico wants a domestic gas storage option that can offer attractive prices that don’t include transport adders, like users must now pay to import gas from the U.S. But it will be difficult to compete with the U.S. storage market, which is the largest and most dynamic in the world. Existing U.S. gas storage sites are immense, with a working capacity of ~4,700 Bcf at 385 storage fields. Many of these have been operating for decades and enhance liquidity by offering short-term contracts.
The U.S. South Central is the closest source of storage for Mexico, and the region’s working gas in storage currently sits at 703 Bcf, which is 293 Bcf lower than this time last year and 199 Bcf below the previous five-year average. And opening up more opportunities for American sellers, U.S. gas pipeline gas capacity into Mexico will reach 15 Bcf/d by 2020, a 50 percent rise from today.
But Mexico’s deregulation is about upgrading energy security with increased self-sufficiency, not spiraling dependence on the U.S. Andrés Manuel López Obrador, the current favorite for Mexico’s July presidential election, has made this clear and has suggested a return to the old days of resource nationalism. Mexico also realizes that the huge U.S. LNG export build-out means that loads of gas will be leaving the country, destined for the booming markets in Asia. Both China and India have proven willing to pay more for energy and sign long-term contracts to ensure supply.
As such, the good news is that Mexico’s recent reforms have widened investment opportunities and brought in new producers. For example, although still small-scale, there are now about 18 non-Pemex and non-CFE gas sellers in the nation. And with an EIA-reported 550,000 Bcf of recoverable shale gas, development should start in Mexico in the early-2020s, especially bolstered by more suppliers, rising prices, and enhanced security against narco-traffickers.
Additionally, current and potential non-state producers were encouraged by Mexico’s Energy Regulatory Commission’s (CRE) decision last June to eliminate the maximum price that natural gas can be sold at “first-hand sales.” Freed from the hands of state control, this is another step for the immature market to finally incorporate the true value of natural gas — increasingly Mexico’s most vital fuel.